Hazardous Waste Combustors
Hazardous waste combustors are defined as process equipment that oxidize hazardous waste, such as cement kilns, waste incinerators, and solid/liquid waste fueled boilers. Combustors meeting this description are regulated by the National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP), as documented in 40 CFR 63 Part EEE. Combustors are regulated for dioxin/furans, mercury, heavy metals, particulate matter, and carbon monoxide.
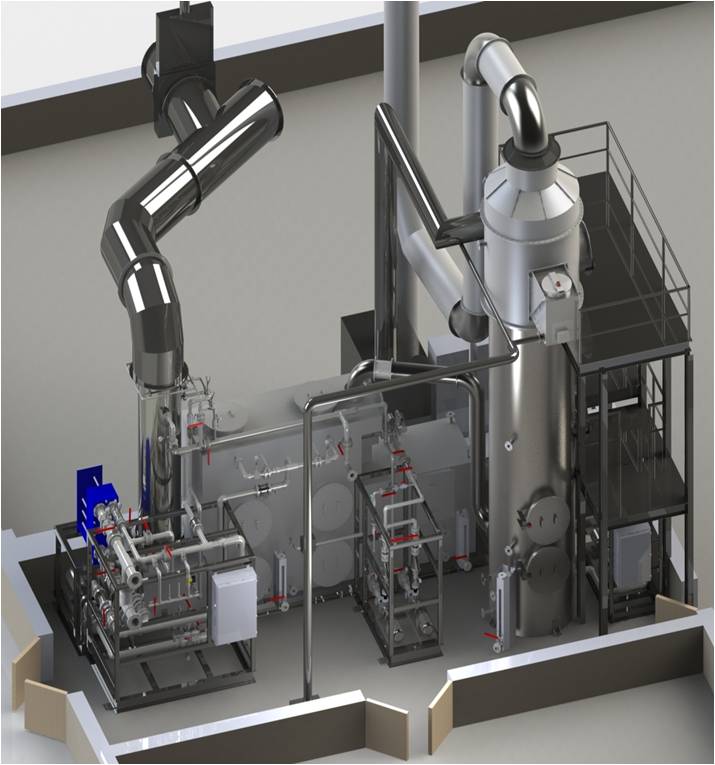
Flue gases from hazardous waste combustors are typically hot, moist, corrosive and particulate-laden. Gas cleanup to meet the strict NESHAP limits requires a well-designed air pollution control train. Typically this train includes: a quencher for cooling the gas, a condenser-absorber for subcooling the gas and absorbing acids, a Venturi scrubber for particulate capture, a wet electrostatic precipitator or filter package for heavy metal removal, and a carbon filter for mercury adsorption.
Envitech has supplied over 100 air pollution control systems to operators of hazardous waste combustors and related incinerators. Envitech has the experience to select the right train to meet the difficult requirements of NESHAP and the stack test results to guarantee it.
NESHAP MACT Standard: Hazardous Waste Combustors, subpart EEE
Exhaust Sources:
- Hazardous Waste Combustors
Pollutants:
- Particulate: (PM)
- Heavy metals: Lead (Pb), Cadmum (Cd), Mercury (Hg),
- Dioxin/Furans
- Acid gases: HCl, SO2
Equipment: