Last March I gave a paper and presentation at the International Conference on Thermal Treatment Technologies and Hazardous Waste Combustors (IT3/HWC) in Houston, TX. The paper discusses the challenges for meeting ultra-low emission limits for medical waste incinerators.  Wet scrubbers are used to control hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) on many hospital, medical, and infectious waste incinerators (HMIWI). The Maximum Available Control Technology (MACT) standard for these incinerators was revised and became final in 2009. The new standard has the lowest emission limits for incinerators today. The limits exceeded the capability of systems designed to the previous standard with respect to particulate matter (PM), lead (Pd), cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg), and dioxin/furans (D/F). By 2014 all existing medical waste incinerators were either shut down or upgraded to comply with the new standard. Envitech successfully upgraded four existing medical waste incinerators. A paper presented at the 2012 IT3/HWC conference describes one of these systems which was installed at the National Institute of Health (NIH), Rocky Mountain Labs.
Wet scrubbers are used to control hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) on many hospital, medical, and infectious waste incinerators (HMIWI). The Maximum Available Control Technology (MACT) standard for these incinerators was revised and became final in 2009. The new standard has the lowest emission limits for incinerators today. The limits exceeded the capability of systems designed to the previous standard with respect to particulate matter (PM), lead (Pd), cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg), and dioxin/furans (D/F). By 2014 all existing medical waste incinerators were either shut down or upgraded to comply with the new standard. Envitech successfully upgraded four existing medical waste incinerators. A paper presented at the 2012 IT3/HWC conference describes one of these systems which was installed at the National Institute of Health (NIH), Rocky Mountain Labs.
The challenge moving fo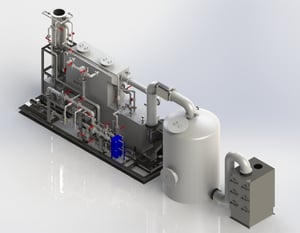 rward will be new medical waste incinerators which have even more stringent, ultra-low emission limits. Building a new incinerator requires critical decisions on control technologies and permitting. The IT3/HWC paper reviews these issues for specific HAPs and discuss trade-offs between permitting a new medium size incinerator versus a large incinerator. An example is provided of an air pollution control system meeting the emission requirements for a new large medical waste incinerator at the University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB) in Galveston, TX. Envitech is also building gas cleaning systems for two new medium size medical waste incinerators for a research facility which integrate NOx control using ozone injection.
rward will be new medical waste incinerators which have even more stringent, ultra-low emission limits. Building a new incinerator requires critical decisions on control technologies and permitting. The IT3/HWC paper reviews these issues for specific HAPs and discuss trade-offs between permitting a new medium size incinerator versus a large incinerator. An example is provided of an air pollution control system meeting the emission requirements for a new large medical waste incinerator at the University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB) in Galveston, TX. Envitech is also building gas cleaning systems for two new medium size medical waste incinerators for a research facility which integrate NOx control using ozone injection.
Please click on the links below download the presentation and paper.