 In 2009, the US EPA revised the emission limits for the Hospital, Medical, and Infectious Waste Incinerator (HMIWI) MACT standard. You can follow the link to the blog piece published in May 2013 on the new standard. It dramatically reduced the emission limits for several pollutants including particulate (PM), lead (Pb), and dioxins and furans (D/F). Several existing medical waste incinerators in operation at the time were not capable of meeting the new limits, especially for lead (Pb) and/or dioxin and furans (D/F). Cost effective add-on controls were needed to bring existing system into compliance with the new rules and to allow them to continue to operate.
In 2009, the US EPA revised the emission limits for the Hospital, Medical, and Infectious Waste Incinerator (HMIWI) MACT standard. You can follow the link to the blog piece published in May 2013 on the new standard. It dramatically reduced the emission limits for several pollutants including particulate (PM), lead (Pb), and dioxins and furans (D/F). Several existing medical waste incinerators in operation at the time were not capable of meeting the new limits, especially for lead (Pb) and/or dioxin and furans (D/F). Cost effective add-on controls were needed to bring existing system into compliance with the new rules and to allow them to continue to operate.
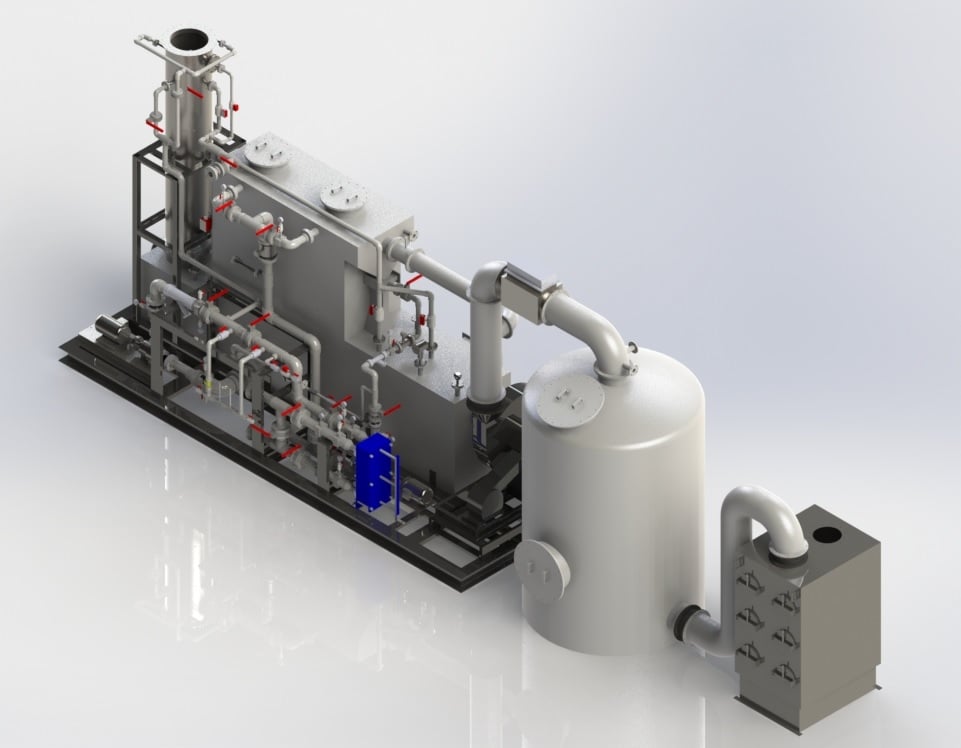
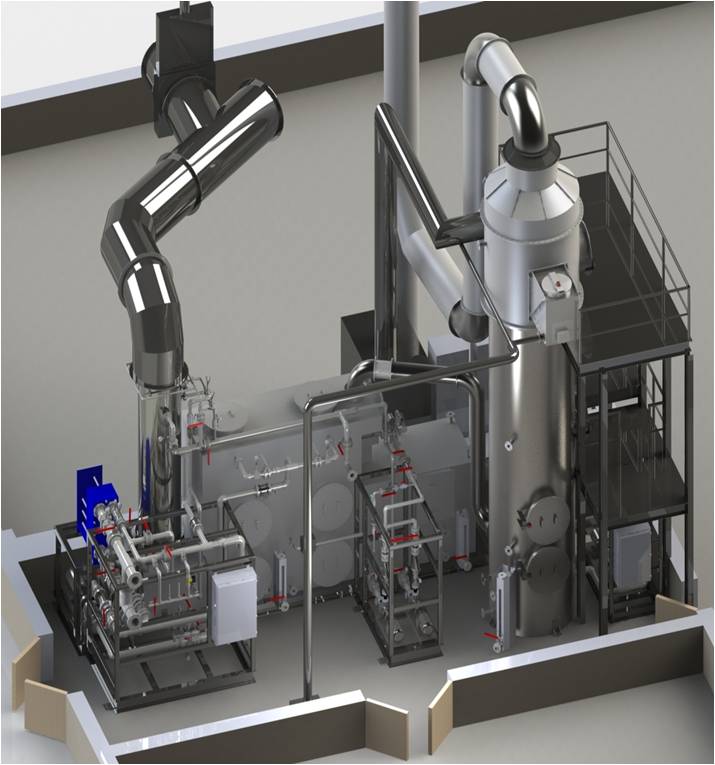
To meet this new challenge, Envitech designed a carbon bed adsorber and filter package to be installed downstream of existing wet scrubbers. The package is comprised of a new fan to overcome additional system pressure drop. Heat of compression from the fan and a re-heater duct heats the wet gas above the dew point to prevent condensation fouling in downstream filter and/or carbon bed adsorber. The system is delivered pre-assembled on a skid to reduce installation time and cost. A cartridge filter removes low concentrations of condensed Pb particulate. The carbon bed adsorber removes dioxins, furans and mercury (Hg). Envitech has upgraded four medical waste incinerators to meet the new MACT standards. All four are operational and compliant with the new standards.
In one case for Wyoming Medical Center (WMC), space was limited for add-on controls. The system had to be installed outdoors and capable of withstanding below freezing temperatures. The existing system did not meet the new limits for lead (Pb) and dioxins/furnace (D/F).The add-on controls included a cartridge filter and a carbon bed adsorber. The equipment was insulated and heat traced to maintain temperature above the dew point after re-heat. System features include:
- Shop and skid mounted assembly for ease of installation.
- Insulation and heat tracing for outdoor operation in a cold climate.
- Silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) controller to control the heater duct.
- Compressed air pulse cleaning for automatic particulate removal from the cartridge filters.
- Pre-wired instrumentation to a control box located on the skid.
- Manways to facilitate maintenance access.
The system has been operational since 2014 and has been used on a routine basis during cold winter months. The system comfortably passed a stack test in 2015. Compliance for lead (Pd) is 20 times below the limit and Dioxins/Furans (D/F) is 5 times below the limit. The re-heat and filter package has been used on several other medical waste incinerators and provide a cost effective solution for meeting stringent emission limits.
Download a free case study to find out how Wymoming Medical Center met the new EPA HMIWI emission limits for their existing medical waste incinerator.
Download a free white paper from the 2010 Internationa Conference on Thermal Treatment Technologies and Hazardous Waste Combustors (IT3/HWC) on the 2009 HMIWI MACT standard for medicl waste incinerators.



 A Venturi scrubber is a common air pollution control device that is used to remove particulate. Because it is a wet scrubber, collected particulate is purged in a liquid discharge stream called the blowdown.
A Venturi scrubber is a common air pollution control device that is used to remove particulate. Because it is a wet scrubber, collected particulate is purged in a liquid discharge stream called the blowdown.

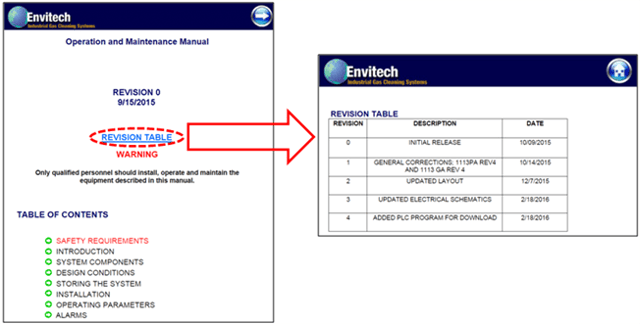
 present several problems – they may be easily lost or damaged; large three-ring binders that are difficult to search and cumbersome to carry; and lastly, red-lined changes and as-builts often are not captured in the final revision.
present several problems – they may be easily lost or damaged; large three-ring binders that are difficult to search and cumbersome to carry; and lastly, red-lined changes and as-builts often are not captured in the final revision.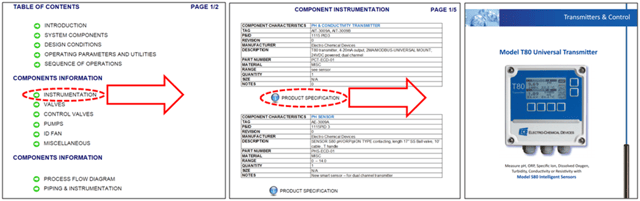

 paper at the International Conference of Thermal Treatment
paper at the International Conference of Thermal Treatment 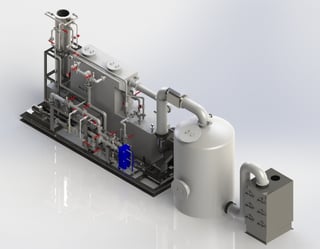 Technologies and Hazardous Waste Combustors (
Technologies and Hazardous Waste Combustors ( Pb reduction for a new large medical waste incinerator is even more dramatic. The emission limit is a mere 0.06% of the 1997 standard. Compared to an existing system permitted to the new standard, a large new medical waste incinerator must emit 2 orders of magnitude less Pb.
Pb reduction for a new large medical waste incinerator is even more dramatic. The emission limit is a mere 0.06% of the 1997 standard. Compared to an existing system permitted to the new standard, a large new medical waste incinerator must emit 2 orders of magnitude less Pb. Compliance testing often brings anxiety to environmental managers. Testing is expensive and can comprise a significant fraction of the environmental operating budget. Planning takes several months, often culminating in a tight testing window with long days and unforeseen delays. And always looming is a dreaded phone call of a failed test. What three things should environmental managers do to ensure a successful compliance test?
Compliance testing often brings anxiety to environmental managers. Testing is expensive and can comprise a significant fraction of the environmental operating budget. Planning takes several months, often culminating in a tight testing window with long days and unforeseen delays. And always looming is a dreaded phone call of a failed test. What three things should environmental managers do to ensure a successful compliance test?
 Envitech is proud to launch a new scrubber service and maintenance program for all users of air pollution control equipment. Envitech offers the program to provide plant managers, environmental departments, plant engineering and operations and maintenance staffs access to our trained, experienced group of engineers and technicians. Our goal is to improve your uptime, reduce your operating costs, ensure you meet compliance and offer you an on-demand technical resource for troubleshooting your equipment. Additionally, we want to help you organize your maintenance programs and provide training to keep your operators up to date.
Envitech is proud to launch a new scrubber service and maintenance program for all users of air pollution control equipment. Envitech offers the program to provide plant managers, environmental departments, plant engineering and operations and maintenance staffs access to our trained, experienced group of engineers and technicians. Our goal is to improve your uptime, reduce your operating costs, ensure you meet compliance and offer you an on-demand technical resource for troubleshooting your equipment. Additionally, we want to help you organize your maintenance programs and provide training to keep your operators up to date.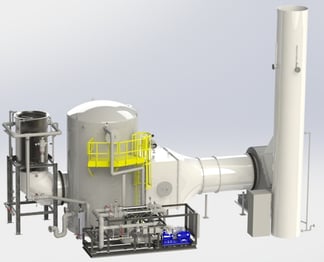

 ogram
ogram
 incinerator. The incinerator exhaust is ducted to a metal quencher (shown in the foreground). The hot gas enters the top of the quencher and flows vertically downward. The gas then elbows into the bottom of a vertical packed bed scrubber (shown in the background). The gas passes upward through the packed bed as re-circulated water flows downward, counter-current to the gas from the top of the packed bed. Water from the quencher and packed bed is collected in the sump and re-circulated back to the quencher and packed bed. An entrainment separator at the top of the scrubber removes entrained water droplets. After exiting the scrubber vessel, an interconnect duct transports the gas to a induced draft fan located at grade.
incinerator. The incinerator exhaust is ducted to a metal quencher (shown in the foreground). The hot gas enters the top of the quencher and flows vertically downward. The gas then elbows into the bottom of a vertical packed bed scrubber (shown in the background). The gas passes upward through the packed bed as re-circulated water flows downward, counter-current to the gas from the top of the packed bed. Water from the quencher and packed bed is collected in the sump and re-circulated back to the quencher and packed bed. An entrainment separator at the top of the scrubber removes entrained water droplets. After exiting the scrubber vessel, an interconnect duct transports the gas to a induced draft fan located at grade.

